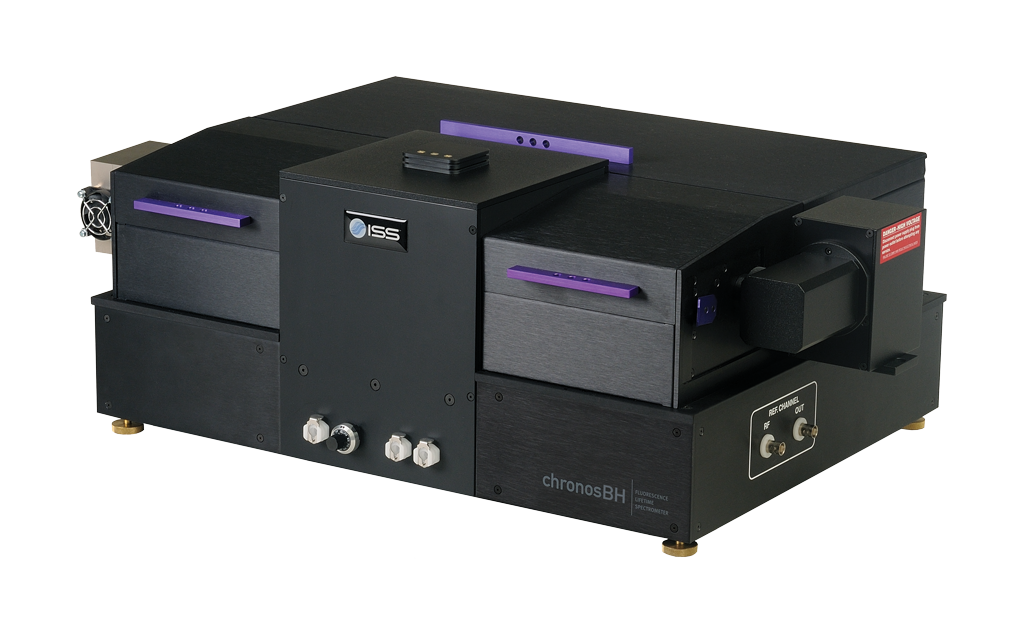
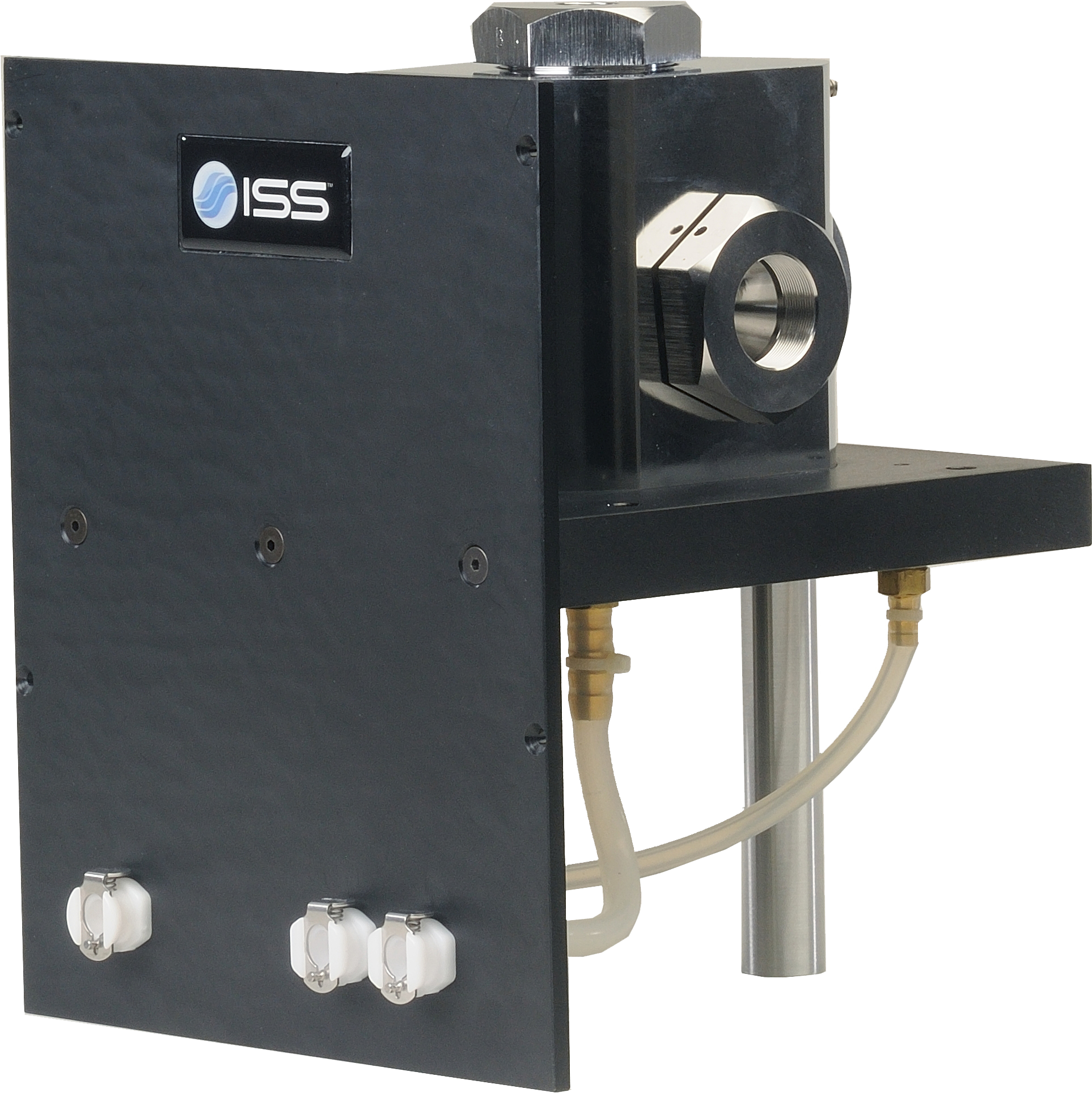
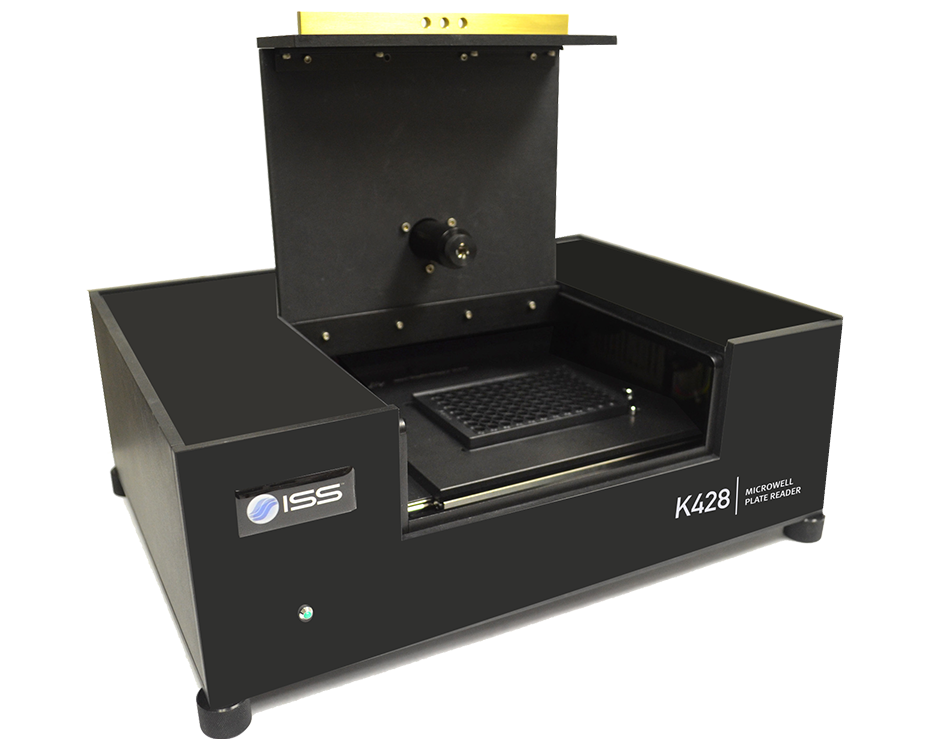
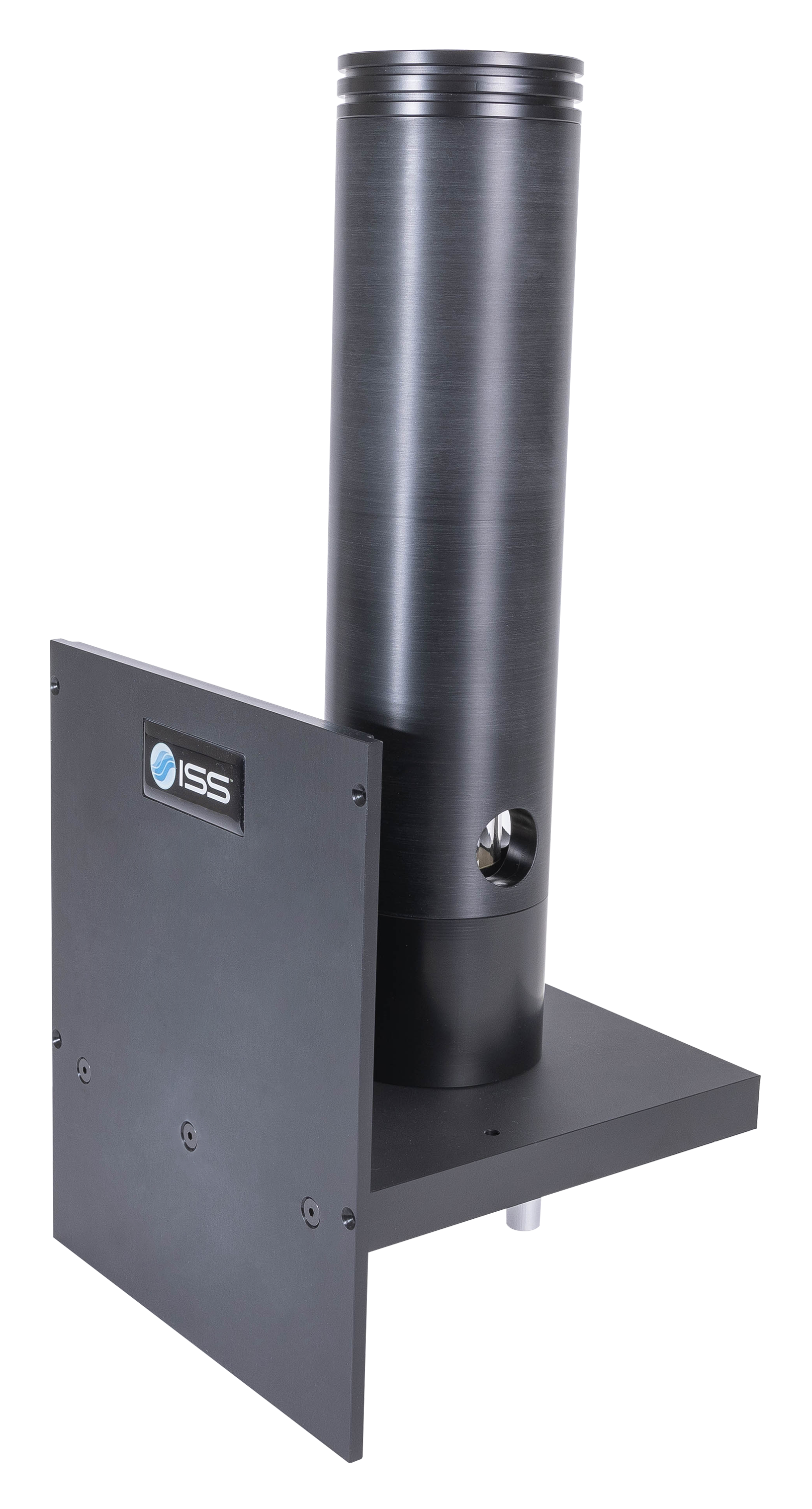
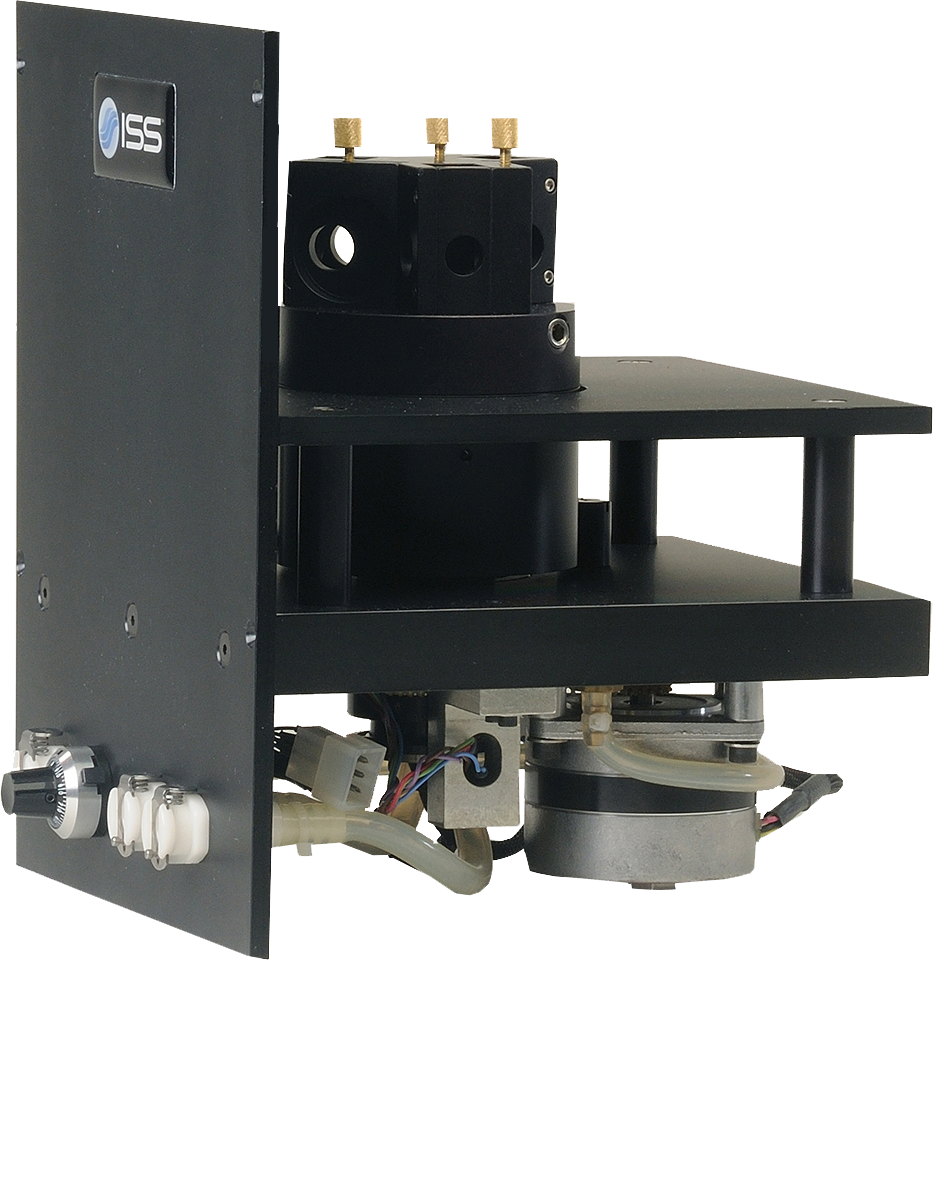
Overview of ChronosBH
ChronosBH is a time-domain (TCSCP) compact spectrometer for decay time measurements over a wide time scale, from picosecond to seconds. The instrument design features a T-format geometry for simultaneous acquisition on two emission channels. A variety of pulsed light sources can be coupled to ChronosBH including laser diodes, supercontinuum laser and multiphoton lasers. Detectors options include fast PMTs, hybrid PMTs and GaAs PMT. The instrument can be upgraded to steady-state fluorescence measurements using a xenon arc lamp.
The ChronosBH operations are fully automated; instrument control, data acquisition and processing are done through Vinci, the Multi-dimentional Spectroscopy software.
Key Features of ChronosBH

Time-Domain Measurements

Maximum Sensitivity

Fully Automated

Integration of External Devices

Upgradeable
- Flexible instrument configuration with a variety of light sources
- A compact footprint, T-format geometry for simultaneous measurements on two channels
- Lifetime measurements from the picosecond to the second
- Full automation of instrument components including: cuvette holder, polarizers, shutters, filterwheel, monochromators and stirrers
- PC-controlled integration of temperature bath, titrator, stopped-flow apparatus and pressure pump
- Upgradable to include steady-state measurements
- Parallel beam optical design for fast and precise polarization measurements
Key Characteristics of Data Acquisition Via Time-Domain
- Is a more direct way of measuring lifetime
- Requires no reference but measurement of an instrument response function (IRF)
- Anisotropy decay measurements require two separate measurements at each plane of polarization
Product Specifications for ChronosBH
Light Source
- Laser diodes (nm): 370, 405, 436, 473, 635, 690, 780, 830
- LEDs (nm): 280, 300, 335, 345, 460, 500, 520
- Pulsed Lasers: Supercontinuum, Ti:Sapphire, Pulsed Laser Diodes
Focusing & Collection Geometry
- Parallel beam design for precise polarization measurements
Polarizers
- UV grade Glan-Thompson with L/A = 2.0
Detectors
- PMTs
- Hybrid PMT, APD
Detection Modes
- Fast analog and photon-counting electronics
Wavelength Range
- 185 - 1,700 (detector dependent)
TCSPC Modules
- Minimum time bin width (ps): 1
- Time resolution, RMS jitter (ps): 34
- Total Counts rate: up to 8.5 MHz
Lifetime Measurements Range
- 10-11 s to 102 s
Operating System
- Windows 11
Power Requirements
- 110 - 240 V, 50/60 Hz, 400 VAC
Dimensions
- 540 mm (L) x 425 mm (W) x 235 mm (H)
Weight (kg)
- 25
Example Configuration for ChronosBH

Product Accessories for ChronosBH
Product Software for ChronosBH

Vinci
A comprehensive multidimensional fluorescence spectroscopy software program designed to enhance the capabilities and performance of ISS spectrofluorometers.
Learn MoreProduct Resources
-
Anisotropy Decay Measurements
-
Fluorescence Basic Instrumentation
-
Fluorescence Lifetime
-
Fluorescence Polarization
-
Fluorescence Spectroscopy
-
Long-Wavelength Polarization Standards
-
Measurement of Fluorescence Quantum Yields on ISS Instrumentation Using Vinci
-
Polarization Measurements: Parallel vs. Non-Parallel Beam Geometry
-
Phasor Plots for the Analysis of Time-resolved Fluorescence
-
What is Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence (TIRF)?
-
A Critical Comparison of Xenon Lamps
-
“Clinically Divergent Mutation Effects on the Structure and Function of the Human Cardiac Tropomyosin Overlap.” Mcconnell, M., Grinspan, L.T., Williams, M.R., Lynn, M.L., Schwartz, B.A., Fass, O.Z., Schwartz, S.D. & Tardiff, J.C. Biochemistry, 56(26), pp. 3403–3413, 2017, Jun. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00266.
-
“Interaction of Hydralazine with Human Serum Albumin and Effect of Β-Cyclodextrin on Binding: Insights from Spectroscopic and Molecular Docking Techniques.” Bolattin, M.B., Nandibewoor, S.T., Joshi, S.D., Dixit, S.R. & Chimatadar, S.A. Industrial Engineering Chemistry Research, 55(19), pp. 5454–5464, 2016, May. doi: 10.1021/acs.iecr.6b00517.
-
“Without Binding ATP, Human Rad51 Does Not Form Helical Filaments on ssDNA.” Schay, G., Borka, B., Kernya, L., Bulyáki, É., Kardos, J., Fekete, M. & Fidy, J. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 120(9), pp. 2165–2178, 2016, Mar. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b12220.
-
“Hydroxymethylation of DNA influences nucleosomal conformation and stability in vitro.” Mendonca, A., Chang, E.H., Liu, W. & Yuan, C. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta - Gene Regulatory Mechanisms, 1839(11), pp. 1323–1329, 2014, Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2014.09.014.
-
“Solution Scattering and FRET Studies on Nucleosomes Reveal DNA Unwrapping Effects of H3 and H4 Tail Removal.” Andresen, K., Jimenez-Useche, I., Howell, S.C., Yuan, C. & Qiu, X. PLoS ONE, 8(11), p. e78587, 2013, Nov. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078587.
-
“DNA Methylation Regulated Nucleosome Dynamics.” Jimenez-Useche, I., Ke, J., Tian, Y., Shim, D., Howell, S.C., Qiu, X. & Yuan, C. Scientific Reports, 3(1), p. e78587, 2013, Jul. doi: 10.1038/srep02121.
-
“The Effect of DNA CpG Methylation on the Dynamic Conformation of a Nucleosome.” Jimenez-Useche, I. & Yuan, C. Biophysical Journal, 103(12), pp. 2502–2512, 2012, Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.11.012.
-
“Conformational Dynamics of Titin PEVK Explored with FRET Spectroscopy.” Huber, T., Grama, L., Hetényi, C., Schay, G., Fülöp, L., Penke, B. & Kellermayer, M. Biophysical Journal, 103(7), pp. 1480–1489, 2012, Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2012.08.042.
-
“Clipping of Flexible Tails of Histones H3 and H4 Affects the Structure and Dynamics of the Nucleosome.” Nurse, N.P., Jimenez-Useche, I., Smith, I.T. & Yuan, C. Biophysical Journal, 104(5), pp. 1081–1088, 2013, Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2013.01.019.
-
“Photophysical and Electrochemical Characterization of BODIPY-Containing Dyads Comparing the Influence of an A–D–A versus D–A Motif on Excited-State Photophysics.” Hendel, S.J., Poe, A.M., Khomein, P., Bae, Y., Thayumanavan, S. & Young, E.R. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A, 120(44), pp. 8794–8803, 2016, Nov. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpca.6b06590.
-
“Photophysical characterization of [Ir(ppy)2(dmb)][PF6] towards application in light-emitting electrochemical cells (LECs).” Zanoni, K.P.S., Sanematsu, M.S. & Iha, N.Y.M. Inorganic Chemistry Communications, 43(44), pp. 162–164, 2014, May. doi: 10.1016/j.inoche.2014.02.010.
-
“Solid State Molecular Device Based on a Rhenium(I) Polypyridyl Complex Immobilized on TiO2 Films.” Patrocinio, A.O.T., Frin, K.P.M. & Iha, N.Y.M. Inorganic Chemistry, 52(10), pp. 5889–5896, 2013, May. doi: 10.1021/ic3028572.
-
“A Pyrene Maleimide with a Flexible Linker for Sampling of Longer Inter-Thiol Distances by Excimer Formation.” Niwayama, S., Kassar, A.S., Zhao, T., Sutton, R.B. & Altenberg, G.A. PLoS ONE, 6(10), p. e26691, 2011, Oct. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026691.
-
“Chlorin-Based Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework Systemically Rejects Colorectal Cancers via Synergistic Photodynamic Therapy and Checkpoint Blockade Immunotherapy.” Lu, K., He, C., Guo, N., Chan, C., Ni, K., Weichselbaum, R.R. & Lin, W. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 138(38), pp. 12502–12510, 2016, Sep. doi: 10.1021/jacs.6b06663.
-
“A Chlorin-Based Nanoscale Metal–Organic Framework for Photodynamic Therapy of Colon Cancers.” Lu, K., He, C. & Lin, W. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 137(24), pp. 7600–7603, 2015, Jun. doi: 10.1021/jacs.5b04069.
-
“Auto-fluorescence lifetime and light reflectance spectroscopy for breast cancer diagnosis: potential tools for intraoperative margin detection.” Sharma, V., Shivalingaiah, S., Peng, Y., Euhus, D., Gryczynski, Z. & Liu, H. Biomedical Optics Express, 3(8), p. 1825, 2012, Jul. doi: 10.1364/boe.3.001825.
-
“A DUAL-MODALITY OPTICAL BIOPSY APPROACH FOR IN VIVO DETECTION OF PROSTATE CANCER IN RAT MODEL.” Sharma, V., Patel, N., Shen, J., Tang, L., Alexandrakis, G. & Liu, H. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences, 04(03), pp. 269–277, 2011, Jul. doi: 10.1142/s179354581100154x.
-
“Efficient and thermally stable inverted perovskite solar cells by introduction of non-fullerene electron transporting materials.” Heo, J.H., Lee, S.-C., Jung, S.-K., Kwon, O.-P. & Im, S.H. J. Mater. Chem. A, 5(39), p. 20615–20622, 2017. doi: 10.1039/c7ta06900f.
-
“Scalable Ligand-Mediated Transport Synthesis of Organic–Inorganic Hybrid Perovskite Nanocrystals with Resolved Electronic Structure and Ultrafast Dynamics.” Wang, L., Williams, N.E., Malachosky, E.W., Otto, J.P., Hayes, D., Wood, R.E., Guyot-Sionnest, P. & Engel, G.S. ACS Nano, 11(3), pp. 2689–2696, 2017, Feb. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.6b07574.
-
“Exploring an Emissive Charge Transfer Process in Zero-Twist Donor–Acceptor Molecular Design as a Dual-State Emitter.” Kumar, S., Singh, P., Kumar, P., Srivastava, R., Pal, S.K. & Ghosh, S. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 120(23), pp. 12723–12733, 2016, Jun. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.6b01351.