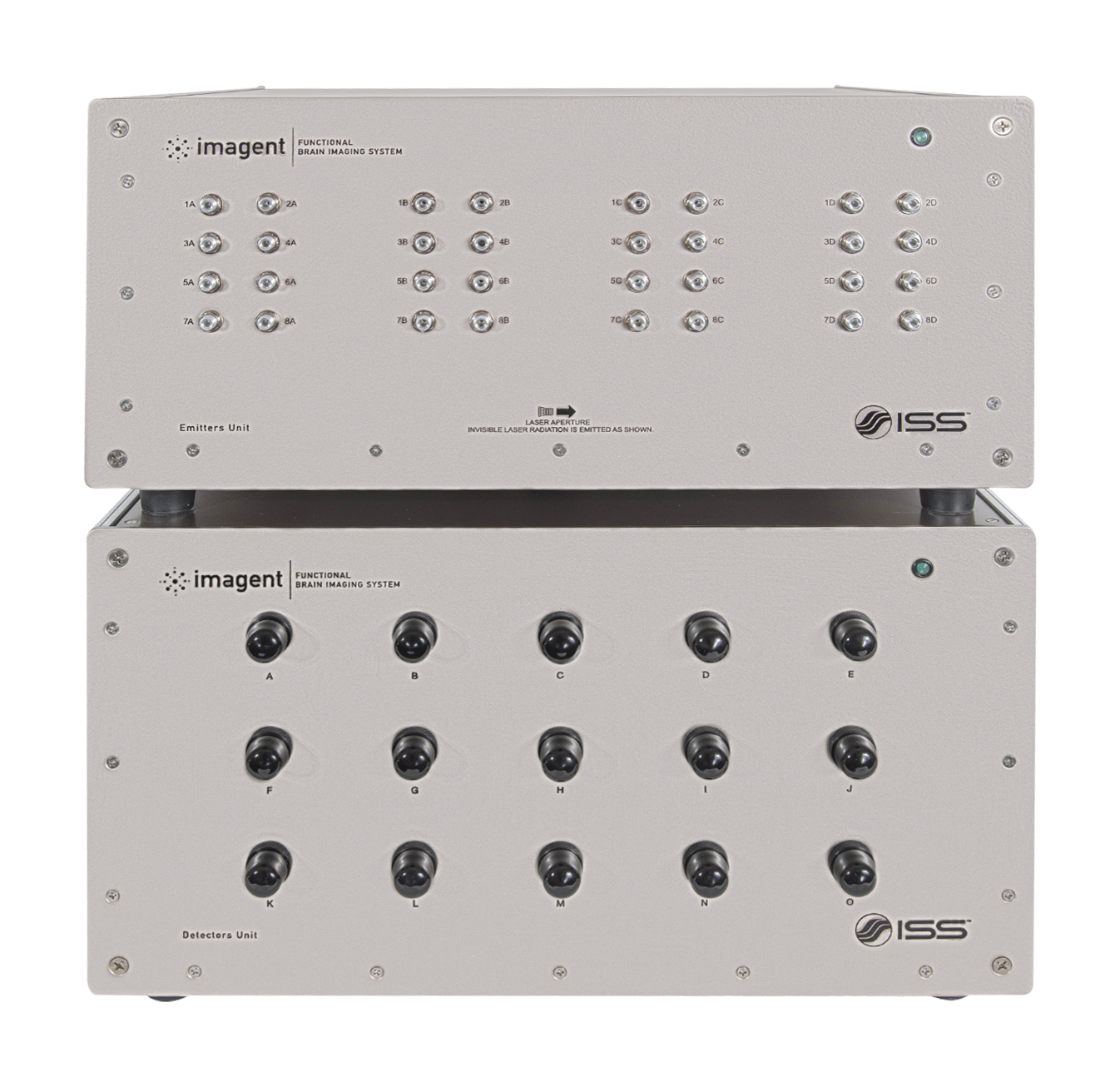
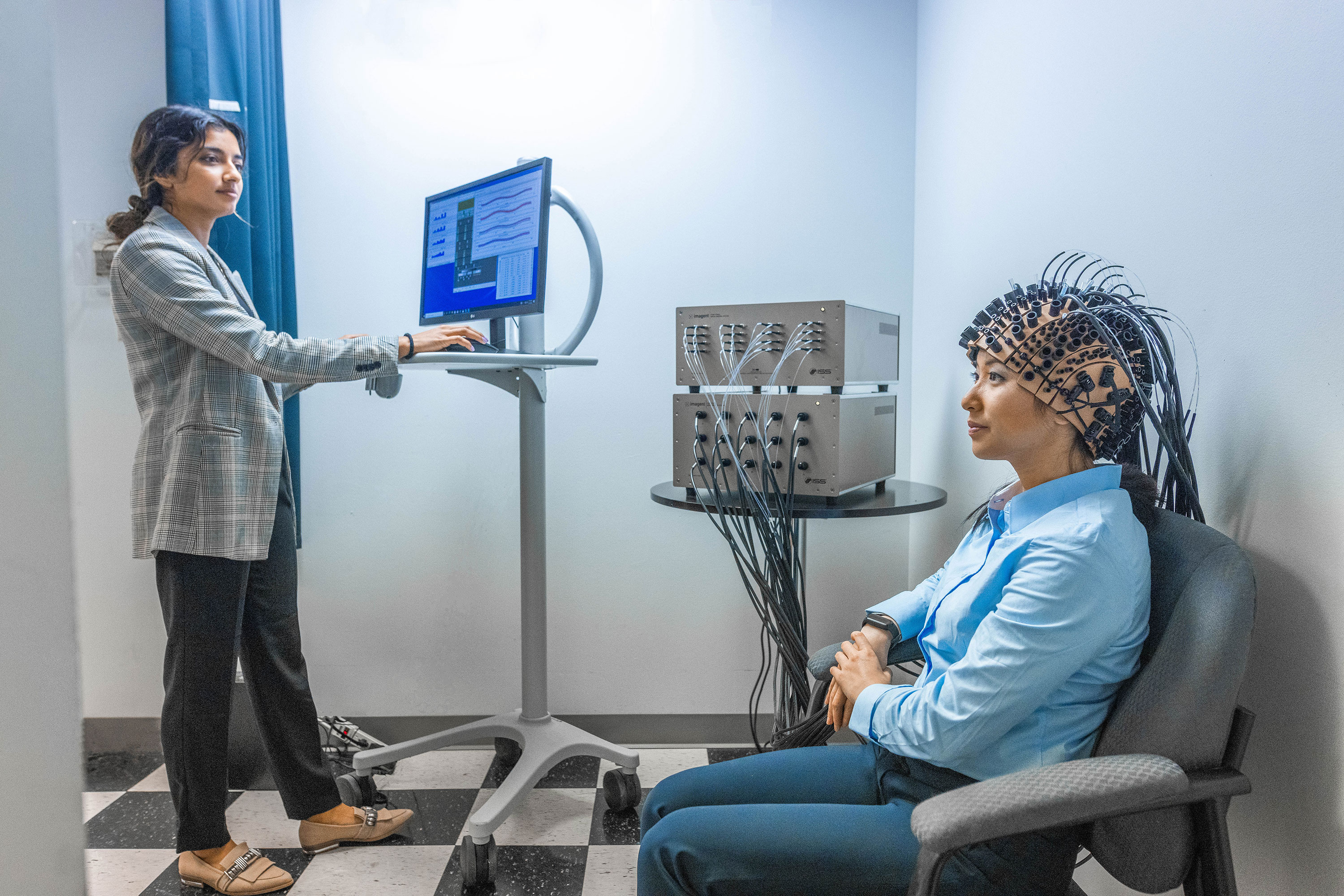
Overview of Imagent
Imagent provides a balance between temporal and spatial resolution for the cognitive study of superficially located areas of human brain by addressing two main applications techniques:
- Functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy (fNIRS), which detects changes in the absorption of the optical signal in response to a stimulus and provides a map of the areas where the changes occur. The changes in the optical signal (time scale > 100 ms), are due to local variations of oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin concentrations.
- Event Related Optical Signal (EROS), which detects changes in the scattered component of the diffuse signal subsequent to a stimulus. The changes (time scale < 100 ms) are due to the variation in the shape of the glia and neurons and/or in the optical properties of the membrane.
Brain imaging techniques can be broadly classified in two groups. One group includes the techniques that have a good spatial resolution (up to 1 - 2 mm) but a poor temporal resolution, such as functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET). The second group includes techniques featuring an excellent temporal resolution (of the order of milliseconds) but providing a limited spatial information. This group includes the Event Related Brain Potential (ERP) and the Magneto-encephalography (MEG). Imagent captures both the slow signals (hemodynamic changes) and the fast signals (EROS).
Notice: Investigational device. Limited by Federal (or United States) law to investigational use. The ISS Imagent is presently used for research only.
Key Features of Imagent

Measures Both Amplitude & Changes in Average Transit Time

Fast Measurements Up to 50 Hz

Applicable to a Wide Range of Research
Applications for Imagent
fNIRS
Cognitive Neuroscience
- Auditory cortex
- Motor cortex
- Visual cortex
- Language centers
Physiological monitoring
- Stress studies
- Working memory in aging
- Mapping epileptic areas in the brain
Virtual Reality
Brain Computer Interface
EROS
Cognitive Neuroscience
- Auditory cortex
- Motor cortex
- Visual cortex
- Language centers
How Imagent Works
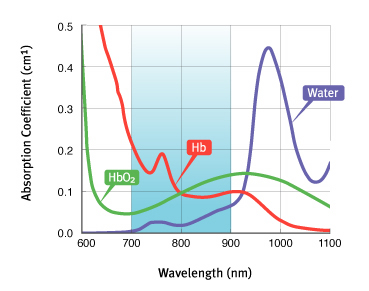
Imagent's working principle is based on the use of near infrared light for probing the cortical surface. The main tissue absorbers in the wavelength region spanning from 700 nm to 900 nm are oxy-hemoglobin (HbO2) and deoxy-hemoglobin (Hb); on a smaller scale, water, fat and cytochrome oxidase contribute to the partial absorption of the light. The penetration depth of light in tissues is quite significant in this wavelength range. For typical head tissue (skin/scalp, skull and cortical layer), with an absorption coefficient of μa = 0.1 cm-1 and a scattering coefficient μs' = 8 cm-1, the maximum optical penetration can be estimated to be about 1.5 cm when a detector is placed at 4 cm from the source. The penetration depth can be increased by increasing the distance between the source and the detector, although, eventually, the signal-to-noise ratio of the measurement deteriorates.
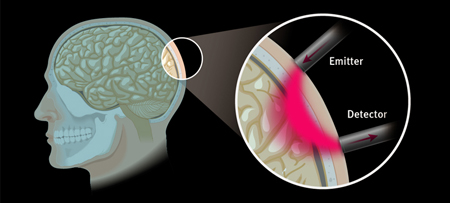
Imagent utilizes laser diodes emitting at 690 nm and 830 nm. The light is delivered by fiber optics positioned on the head. Upon entering the tissue, the near infrared light, albeit weakly absorbed, is highly scattered by the tissue in homogeneities. A fraction of the light leaves the tissue and it is collected by the collecting fiber that carries it back to the light detectors housed in the unit for data processing. The fibers are kept in place by a headgear, which is available for adults and children; for the study of specific areas, pad sensors are available. Up to 128 fibers and up to 60 detectors bundles (for a total of 3,840 optical channels) can be positioned on the head of an adult. Different patterns (montages) of the excitation and collection fibers can be used.
Imagent utilizes the frequency domain technology; whereas, the light sources are modulated at high frequency (of the order of 100 MHz) and three parameters of the detected signal are measured: the intensity, the modulation depth and the time it takes to traverse the tissue (phase delay). Any two combinations of the three measured quantities can be utilized to provide changes in the physiological parameters, the choice being dictated by the specific parameter to be measured, by the need to reduce physiological noise and by the time scale of the event to be measured.
Product Specifications for Imagent
Operations
- Method: frequency domain
- Modulation frequency 110 MHz
- Sampling time: minimum 15 ms
- Number of optical channels: 16 to 960
fNIRS Measured Parameters
- Changes in O2Hb oxygenated hemoglobin
- Changes in HHb deoxygenated hemoglobin
- Changes in Hb total hemoglobin
EROS Measured Parameters
- Signal intensity
- Signal phase delay
Light Sources
- Fiber coupled laser diodes
- Wavelengths: 690 nm and 830 nm
- Laser power: 10 mW average
Light Detectors
- Photomultiplier tubes
Optodes
- Paired fibers in excitation, 400 µm diameter
- Fiber bundle in collection, 3 mm diameter
Interface
- Interfaceable to FastTrack by Polhemus for Talairach registration technique of brain coordinates
Pre-Amplifier Discriminators
- 600 MHz bandwidth, TTL output
Computer and Operating System
- Intel-type CPU, Windows 11 operating system
Power Requirements
- Universal power input: 110 - 240 V, 250 W
Product Accessories for Imagent
Product Resources
-
“On the functional role of temporal and frontal cortex activation in passive detection of auditory deviance.” Tse, C.-Y. & Penney, T.B. NeuroImage, 41(4), pp. 1462–1470, 2008, Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2008.03.043.
-
“The role of visual and auditory temporal processing for Chinese children with developmental dyslexia.” Chung, K.K.H., Mcbride-Chang, C., Wong, S.W.L., Cheung, H., Penney, T.B. & Ho, C.S.-H. Annals of Dyslexia, 58(1), pp. 15–35, 2008, May. doi: 10.1007/s11881-008-0015-4.
-
“Optical imaging of temporal integration in human auditory cortex.” Sable, J.J., Low, K.A., Whalen, C.J., Maclin, E.L., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. European Journal of Neuroscience, 25(1), pp. 298–306, 2007, Jan. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2006.05255.x.
-
“Latent inhibition mediates N1 attenuation to repeating sounds.” Sable, J.J., Low, K.A., Maclin, E.L., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. Psychophysiology, 41(4), pp. 636–642, 2004, Jul. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2004.00192.x.
-
“RAPID COMMUNICATION Scalp-Recorded Optical Signals Make Sound Processing in the Auditory Cortex Visible?” Rinne, T., Gratton, G., Fabiani, M., Cowan, N., Maclin, E., Stinard, A., Sinkkonen, J., Alho, K. & Näätänen, R. NeuroImage, 10(5), pp. 620–624, 1999, Nov. doi: 10.1006/nimg.1999.0495.
-
“Functional near-infrared spectroscopy-based correlates of prefrontal cortical dynamics during a cognitive-motor executive adaptation task.” Gentili, R.J., Shewokis, P.A., Ayaz, H. & Contreras-Vidal, J.L. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 2013. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00277.
-
“Number–Space Interactions in the Human Parietal Cortex: Enlightening the SNARC Effect with Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.” Cutini, S., Scarpa, F., Scatturin, P., Dell'Acqua, R. & Zorzi, M. Cerebral Cortex, 24(2), pp. 444–451, 2012, Oct. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs321.
-
“Exploring the role of primary and supplementary motor areas in simple motor tasks with fNIRS.” Brigadoi, S., Cutini, S., Scarpa, F., Scatturin, P. & Dell'Acqua, R. Cognitive Processing, 13(S1), pp. 97–101, 2012, Jul. doi: 10.1007/s10339-012-0446-z.
-
“The cortical control of cycling exercise in stroke patients: An fNIRS study.” Lin, P.-Y., Chen, J.-J.J. & Lin, S.-I. Human Brain Mapping, 34(10), pp. 2381–2390, 2012, Mar. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22072.
-
“When in Doubt, Do it Both Ways: Brain Evidence of the Simultaneous Activation of Conflicting Motor Responses in a Spatial Stroop Task.” Desoto, M.C., Fabiani, M., Geary, D.C. & Gratton, G. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 13(4), pp. 523–536, 2001, May. doi: 10.1162/08989290152001934.
-
“Rapid Changes of Optical Parameters in the Human Brain During a Tapping Task.” Gratton, G., Fabiani, M., Friedman, D., Franceschini, M.A., Fantini, S., Corballis, P. & Gratton, E. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 7(4), pp. 446–456, 1995. doi: 10.1162/jocn.1995.7.4.446.
-
“Early childhood development of visual texture segregation in full-term and preterm children.” Sayeur, M.S., Vannasing, P., Lefrançois, M., Tremblay, E., Lepore, F., Lassonde, M., Mckerral, M. & Gallagher, A. Vision Research, 112, pp. 1–10, 2015, Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2015.04.013.
-
“Comparison of neuronal and hemodynamic measures of the brain response to visual stimulation: An optical imaging study.” Gratton, G., Goodman-Wood, M.R. & Fabiani, M. Human Brain Mapping, 13(1), pp. 13–25, 2001. doi: 10.1002/hbm.1021.
-
“Shades of gray matter: Noninvasive optical images of human brain reponses during visual stimulation.” Gratton, G., Corballis, P.M., Cho, E., Fabiani, M. & Hood, D.C. Psychophysiology, 32(5), pp. 505–509, 1995, Sep. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1995.tb02102.x.
-
“Distinct hemispheric specializations for native and non-native languages in one-day-old newborns identified by fNIRS.” Vannasing, P., Florea, O., González-Frankenberger, B., Tremblay, J., Paquette, N., Safi, D., Wallois, F., Lepore, F., Béland, R., Lassonde, M. & Gallagher, A. Neuropsychologia, 84, pp. 63–69, 2016, Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2016.01.038.
-
“Early electrophysiological markers of atypical language processing in prematurely born infants.” Paquette, N., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., Lefebvre, F., Roy, M.-S., Mckerral, M., Lepore, F., Lassonde, M. & Gallagher, A. Neuropsychologia, 79, pp. 21–32, 2015, Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.10.021.
-
“Developmental patterns of expressive language hemispheric lateralization in children, adolescents and adults using functional near-infrared spectroscopy.” Paquette, N., Lassonde, M., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., González-Frankenberger, B., Florea, O., Béland, R., Lepore, F. & Gallagher, A. Neuropsychologia, 68, pp. 117–125, 2015, Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.01.007.
-
“Functional near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of overt reading.” Safi, D., Lassonde, M., Nguyen, D.K., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., Florea, O., Morin-Moncet, O., Lefrançois, M. & Béland, R. Brain and Behavior, 2(6), pp. 825–837, 2012, Oct. doi: 10.1002/brb3.100.
-
“Morphological Structure Awareness, Vocabulary, and Reading.” McBride-Chang, C., Hua, S., Ng, J.Y.L., Meng, X., & Penney, T.B. Vocabulary Acquisition: Implications for Reading Comprehension, 6, 2007, pp. 104 - 122.
-
“Speeded Naming and Dyslexia.” Penney, T.B., Wong, S., Ng, K.K., & McBride-Chang, C.A. Communicating Skills of Intention, 2007, pp. 75 - 90.
-
“Near-infrared Spectroscopy as an Alternative to the Wada Test for Language Mapping in Children, Adults and Special Populations.” Gallagher, A., Thériault, M., Maclin, E., Low, K., Gratton, G., Fabiani, M., Gagnon, L., Valois, K., Rouleau, I., Sauerwein, H.C., Carmant, L., Nguyen, D.K., Lortie, A., Lepore, F., Béland, R., & Lassonde, M. Epileptic Disord, 9(3), 2007, Sep.
-
“Poor readers of chinese respond slower than good readers in phonological, rapid naming, and interval timing tasks.” Penney, T.B., Leung, K.M., Chan, P.C., Meng, X. & Mcbride-Chang, C.A. Annals of Dyslexia, 55(1), pp. 9–27, 2005, Jun. doi: 10.1007/s11881-005-0002-y.
-
“Brain Responses to Segmentally and Tonally Induced Semantic Violations in Cantonese.” Schirmer, A., Tang, S.-L., Penney, T.B., Gunter, T.C. & Chen, H.-C. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(1), pp. 1–12, 2005, Jan. doi: 10.1162/0898929052880057.
-
“Taking the pulse of aging: Mapping pulse pressure and elasticity in cerebral arteries with optical methods.” Fabiani, M., Low, K.A., Tan, C.-H., Zimmerman, B., Fletcher, M.A., Schneider-Garces, N., Maclin, E.L., Chiarelli, A.M., Sutton, B.P. & Gratton, G. Psychophysiology, 51(11), pp. 1072–1088, 2014, Aug. doi: 10.1111/psyp.12288.
-
“Contributions of Cognitive Neuroscience to the Understanding of Behavior and Aging.” Kramer, A.F., Fabiani, M. & Colcombe, S.J. Handbook of the Psychology of Aging, pp. 57–83, 2006. doi: 10.1016/b978-012101264-9/50007-0.
-
“Reduced Suppression or Labile Memory? Mechanisms of Inefficient Filtering of Irrelevant Information in Older Adults.” Fabiani, M., Low, K.A., Wee, E., Sable, J.J. & Gratton, G. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 18(4), pp. 637–650, 2006, Apr. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2006.18.4.637.
-
“Multiple Electrophysiological Indices of Distinctiveness.” Fabiani, M. Distinctiveness and Memory, pp. 338–360, 2006, Apr. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195169669.003.0015.
-
“Electrophysiological and Optical Measures of Cognitive Aging.” Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. , pp. 85–106, 2004, Dec. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195156744.003.0004.
-
“Sensory ERPs predict differences in working memory span and fluid intelligence.” Brumback, C.R., Low, K.A., Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. NeuroReport, 15(2), pp. 373–376, 2004, Feb. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200402090-00032.
-
“Recruitment of the left precentral gyrus in reading epilepsy: A multimodal neuroimaging study.” Safi, D., Béland, R., Nguyen, D.K., Pouliot, P., Mohamed, I.S., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., Lassonde, M. & Gallagher, A. Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports, 5, pp. 19–22, 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2016.01.003.
-
“Potential brain language reorganization in a boy with refractory epilepsy; an fNIRS–EEG and fMRI comparison.” Vannasing, P., Cornaggia, I., Vanasse, C., Tremblay, J., Diadori, P., Perreault, S., Lassonde, M. & Gallagher, A. Epilepsy & Behavior Case Reports, 5, pp. 34–37, 2016. doi: 10.1016/j.ebcr.2016.01.006.
-
“Using patient-specific hemodynamic response function in epileptic spike analysis of human epilepsy: a study based on EEG–fNIRS.” Peng, K., Nguyen, D.K., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., Lesage, F. & Pouliot, P. NeuroImage, 126, pp. 239–255, 2016, Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.11.045.
-
“Hemodynamic changes during posterior epilepsies: An EEG-fNIRS study.” Pouliot, P., Tran, T.P.Y., Birca, V., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., Lassonde, M. & Nguyen, D.K. Epilepsy Research, 108(5), pp. 883–890, 2014, Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2014.03.007.
-
“fNIRS-EEG study of focal interictal epileptiform discharges.” Peng, K., Nguyen, D.K., Tayah, T., Vannasing, P., Tremblay, J., Sawan, M., Lassonde, M., Lesage, F. & Pouliot, P. Epilepsy Research, 108(3), pp. 491–505, 2014, Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.12.011.
-
“Noninvasive continuous functional near-infrared spectroscopy combined with electroencephalography recording of frontal lobe seizures.” Nguyen, D.K., Tremblay, J., Pouliot, P., Vannasing, P., Florea, O., Carmant, L., Lepore, F., Sawan, M., Lesage, F. & Lassonde, M. Epilepsia, 54(2), pp. 331–340, 2012, Nov. doi: 10.1111/epi.12011.
-
“Nonlinear hemodynamic responses in human epilepsy: A multimodal analysis with fNIRS-EEG and fMRI-EEG.” Pouliot, P., Tremblay, J., Robert, M., Vannasing, P., Lepore, F., Lassonde, M., Sawan, M., Nguyen, D.K. & Lesage, F. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 204(2), pp. 326–340, 2012, Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2011.11.016.
-
“Perception of Caucasian and African faces in 5- to 9-month-old Caucasian infants: A functional near-infrared spectroscopy study.” Timeo, S., Brigadoi, S. & Farroni, T. Neuropsychologia, 126, pp. 3–9, 2019, Mar. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2017.09.011.
-
“Infant cortex responds to other humans from shortly after birth.” Farroni, T., Chiarelli, A.M., Lloyd-Fox, S., Massaccesi, S., Merla, A., Gangi, V.D., Mattarello, T., Faraguna, D. & Johnson, M.H. Scientific Reports, 3(1), 2013, Oct. doi: 10.1038/srep02851.
-
“Coupled oxygenation oscillation measured by NIRS and intermittent cerebral activation on EEG in premature infants.” Roche-Labarbe, N., Wallois, F., Ponchel, E., Kongolo, G. & Grebe, R. NeuroImage, 36(3), pp. 718–727, 2007, Jul. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2007.04.002.
-
“Measurement of brain activity by near-infrared light.” Gratton, E., Toronov, V., Wolf, U., Wolf, M. & Webb, A. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 10(1), p. 011008, 2005. doi: 10.1117/1.1854673.
-
“Noninvasive determination of the optical properties of adult brain: near-infrared spectroscopy approach.” Choi, J., Wolf, M., Toronov, V., Wolf, U., Polzonetti, C., Hueber, D., Safonova, L.P., Gupta, R., Michalos, A., Mantulin, W. & Gratton, E. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 9(1), p. 221, 2004. doi: 10.1117/1.1628242.
-
“Absolute Frequency-Domain Pulse Oximetry of the Brain: Methodology and Measurements.” Wolf, M., Franceschini, M.A., Paunescu, L.A., Toronov, V., Michalos, A., Wolf, U., Gratton, E. & Fantini, S. Oxygen Transport to Tissue, 24, pp. 61–73, 2003. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-0075-9_7.
-
“Fast cerebral functional signal in the 100-ms range detected in the visual cortex by frequency-domain near-infrared spectrophotometry.” Wolf, M., Wolf, U., Choi, J.H., Toronov, V., Paunescu, L.A., Michalos, A. & Gratton, E. Psychophysiology, 40(4), pp. 521–528, 2003, Jul. doi: 10.1111/1469-8986.00054.
-
“Different Time Evolution of Oxyhemoglobin and Deoxyhemoglobin Concentration Changes in the Visual and Motor Cortices during Functional Stimulation: A Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Study.” Wolf, M., Wolf, U., Toronov, V., Michalos, A., Paunescu, L., Choi, J.H. & Gratton, E. NeuroImage, 16(3), pp. 704–712, 2002, Jul. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2002.1128.
-
“Near-infrared study of fluctuations in cerebral hemodynamics during rest and motor stimulation: Temporal analysis and spatial mapping.” Toronov, V., Franceschini, M.A., Filiaci, M., Fantini, S., Wolf, M., Michalos, A. & Gratton, E. Medical Physics, 27(4), pp. 801–815, 2000, Apr. doi: 10.1118/1.598943.
-
“Cerebral hemodynamics measured by near-infrared spectroscopy at rest and during motor activation.” Angela, M., Sergio, F., Sergio, F., Vlad, T., Mattia, F. & Enrico, G. Proceedings of the Optical Society of America In Vivo Optical Imaging Workshop: Washington, pp. 78 - 80, 2000, Jan.
-
“On-line optical imaging of the human brain with 160-ms temporal resolution.” Franceschini, M.A., Toronov, V., Filiaci, M.E., Gratton, E. & Fantini, S. Optics Express, 6(3), p. 49, 2000, Jan. doi: 10.1364/oe.6.000049.
-
“Shades of gray matter: Noninvasive optical images of human brain reponses during visual stimulation.” Gratton, G., Corballis, P.M., Cho, E., Fabiani, M. & Hood, D.C. Psychophysiology, 32(5), pp. 505–509, 1995, Sep. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.1995.tb02102.x.
-
“Dynamic filtering improves attentional state prediction with fNIRS.” Harrivel, A.R., Weissman, D.H., Noll, D.C., Huppert, T. & Peltier, S.J. Biomedical Optics Express, 7(3), p. 979, 2016, Feb. doi: 10.1364/boe.7.000979.
-
“Detection of Attentional State in Long-Distance Driving Settings Using Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.” Matthew, T., Miles, A., V., S., Michael, C. & Mary, C. 95th Annual Transportation Research Board Meeting, 2016, Jan.
-
“Investigating Mental Workload Changes in a Long Duration Supervisory Control Task.” Boyer, M., Cummings, M., Spence, L.B. & Solovey, E.T. Interacting with Computers, 27(5), pp. 512–520, 2015, May. doi: 10.1093/iwc/iwv012.
-
“Monitoring attentional state with fNIRS.” Harrivel, A.R., Weissman, D.H., Noll, D.C. & Peltier, S.J. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience, 7, 2013. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2013.00861.
-
“Learn Piano with BACh.” Yuksel, B.F., Oleson, K.B., Harrison, L., Peck, E.M., Afergan, D., Chang, R. & Jacob, R.J. Proceedings of the 2016 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2016, May. doi: 10.1145/2858036.2858388.
-
“Braahms: a novel adaptive musical interface based on users' cognitive state.” Yuksel, B.F., Afergan, D., Peck, E.M., Griffin, G., Harrison, L., Chen, N.W.B., Chang, R., & Jacob, R.J.K. NIME, pp. 136–139, 2015.
-
“A hybrid NIRS-EEG system for self-paced brain computer interface with online motor imagery.” Koo, B., Lee, H.-G., Nam, Y., Kang, H., Koh, C.S., Shin, H.-C. & Choi, S. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 244, pp. 26–32, 2015, Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2014.04.016.
-
“Brain-based target expansion.” Afergan, D., Shibata, T., Hincks, S.W., Peck, E.M., Yuksel, B.F., Chang, R. & Jacob, R.J. Proceedings of the 27th annual ACM symposium on User interface software and technology, 2014, Oct. doi: 10.1145/2642918.2647414.
-
“Temporal decoupling of oxy- and deoxy-hemoglobin hemodynamic responses detected by functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS).” Tam, N.D. & Zouridakis, G. Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Medical Imaging, 1(2), pp. 18–28, 2014, Apr. doi: 10.14738/jbemi.12.146.
-
“Using fNIRS brain sensing to evaluate information visualization interfaces.” Peck, E.M.M., Yuksel, B.F., Ottley, A., Jacob, R.J. & Chang, R. Proceedings of the SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, 2013, Apr. doi: 10.1145/2470654.2470723.
-
“Classification of prefrontal activity due to mental arithmetic and music imagery using hidden Markov models and frequency domain near-infrared spectroscopy.” Power, S.D., Falk, T.H. & Chau, T. Journal of Neural Engineering, 7(2), p. 026002, 2010, Feb. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/7/2/026002.
-
“Single-trial classification of NIRS signals during emotional induction tasks: towards a corporeal machine interface.” Tai, K. & Chau, T. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation, 6(1), 2009, Nov. doi: 10.1186/1743-0003-6-39.
-
“Taking NIRS-BCIs Outside the Lab: Towards Achieving Robustness Against Environment Noise.” Falk, T.H., Guirgis, M., Power, S. & Chau, T.T. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 19(2), pp. 136–146, 2011, Apr. doi: 10.1109/tnsre.2010.2078516.
-
“A new method based on ICBM152 head surface for probe placement in multichannel fNIRS.” Cutini, S., Scatturin, P. & Zorzi, M. NeuroImage, 54(2), pp. 919–927, 2011, Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.09.030.
-
“Bayesian filtering of human brain hemodynamic activity elicited by visual short-term maintenance recorded through functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS).” Scarpa, F., Cutini, S., Scatturin, P., Dell'Acqua, R. & Sparacino, G. Optics Express, 18(25), p. 26550, 2010, Dec. doi: 10.1364/oe.18.026550.
-
“Validation of a method for coregistering scalp recording locations with 3D structural MR images.” Whalen, C., Maclin, E.L., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. Human Brain Mapping, 29(11), pp. 1288–1301, 2008, Nov. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20465.
-
“Level-set algorithm for the reconstruction of functional activation in near-infrared spectroscopic imaging.” Jacob, M., Bresler, Y., Toronov, V., Zhang, X. & Webb, A. Journal of Biomedical Optics, 11(6), p. 064029, 2006. doi: 10.1117/1.2400595.
-
“Signal and image processing techniques for functional near-infrared imaging of the human brain.” Toronov, V.Y., Zhang, X., Fabiani, M., Gratton, G. & Webb, A.G. SPIE Proceedings, 2005, Mar. doi: 10.1117/12.593345.
-
“Optimization of the frequency-domain instrument for the near-infrared spectro-imaging of the human brain.” Toronov, V.Y., Di Amico, E., Hueber, D., Gratton, E., Webb, A.G. & Barbieri, B.B. SPIE Proceedings, 2004, Jul. doi: 10.1117/12.530254.
-
“Optimization of the signal-to-noise ratio of frequency-domain instrumentation for near-infrared spectro-imaging of the human brain.” Toronov, V., D'Amico, E., Hueber, D., Gratton, E., Barbieri, B. & Webb, A. Optics Express, 11(21), p. 2717, 2003, Oct. doi: 10.1364/oe.11.002717.
-
“Frequency-Domain Techniques for Cerebral and Functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy.” Fantini, S. & Sassaroli, A. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 14, 2020, Apr. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00300.
-
“A brief review on the history of human functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) development and fields of application.” Ferrari, M. & Quaresima, V. NeuroImage, 63(2), pp. 921–935, 2012, Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.03.049.
-
“Detection of event-related hemodynamic response to neuroactivation by dynamic modeling of brain activity.” Aqil, M., Hong, K.-S., Jeong, M.-Y. & Ge, S.S. NeuroImage, 63(1), pp. 553–568, 2012, Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.07.006.
-
“Cortical brain imaging by adaptive filtering of NIRS signals.” Aqil, M., Hong, K.-S., Jeong, M.-Y. & Ge, S.S. Neuroscience Letters, 514(1), pp. 35–41, 2012, Apr. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2012.02.048.
-
“Functional near Infrared Optical Imaging in Cognitive Neuroscience: An Introductory Review.” Cutini, S., Moro, S.B. & Bisconti, S. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 20(1), pp. 75–92, 2012, Jan. doi: 10.1255/jnirs.969.
-
“Near Infrared Brain and Muscle Oximetry: From the Discovery to Current Applications.” Ferrari, M. & Quaresima, V. Journal of Near Infrared Spectroscopy, 20(1), pp. 1–14, 2012, Jan. doi: 10.1255/jnirs.973.
-
“The influence of posterior parietal cortex on extrastriate visual activity: A concurrent TMS and fast optical imaging study.” Parks, N.A., Mazzi, C., Tapia, E., Savazzi, S., Fabiani, M., Gratton, G. & Beck, D.M. Neuropsychologia, 78, pp. 153–158, 2015, Nov. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2015.10.002.
-
“Preattentive change detection using the event-related optical signal.” Tse, C.-Y. & Penney, T.B. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 26(4), pp. 52–58, 2007, Jul. doi: 10.1109/memb.2007.384096.
-
“Event-related optical imaging reveals the temporal dynamics of right temporal and frontal cortex activation in pre-attentive change detection.” Tse, C.-Y., Tien, K.-R. & Penney, T.B. NeuroImage, 29(1), pp. 314–320, 2006, Jan. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.07.013.
-
“Fast optical signal in visual cortex: Improving detection by General Linear Convolution Model.” Chiarelli, A.M., Vacri, A.D., Romani, G.L. & Merla, A. NeuroImage, 66, pp. 194–202, 2013, Feb. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.047.
-
“Time course of activation of human occipital cortex measured with the event-related optical signal (EROS).” Gratton, G., Low, K.A., Maclin, E.L., Brumback, C.R., Gordon, B. & Fabiani, M. Biomedical Optics, 2006. doi: 10.1364/bio.2006.md4.
-
“Fronto-occipital mismatch responses in pre-attentive detection of visual changes: Implication on a generic brain network underlying Mismatch Negativity (MMN).” Tse, C.-Y., Shum, Y.-H., Xiao, X.-Z. & Wang, Y. NeuroImage, 244, p. 118633, 2021, Dec. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118633.
-
“Functional connectivity of the frontotemporal network in preattentive detection of abstract changes: Perturbs and observes with transcranial magnetic stimulation and event-related optical signal.” Xiao, X.-Z., Shum, Y.-H., Lui, T.K.-Y., Wang, Y., Cheung, A.T.-C., Chu, W.C.W., Neggers, S.F.W., Chan, S.S.-M. & Tse, C.-Y. Human Brain Mapping, 41(11), pp. 2883–2897, 2020, Mar. doi: 10.1002/hbm.24984.
-
“Time course of activation of human occipital cortex measured with the event-related optical signal (EROS).” Gratton, G., Low, K.A., Maclin, E.L., Brumback, C.R., Gordon, B. & Fabiani, M. Biomedical Optics, 2006. doi: 10.1364/bio.2006.md4.
-
“Fast optical imaging of frontal cortex during active and passive oddball tasks.” Low, K.A., Leaver, E., Kramer, A.F., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. Psychophysiology, 43(2), pp. 127–136, 2006, Mar. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-8986.2006.00390.x.
-
“Dynamic brain imaging: Event-related optical signal (EROS) measures of the time course and localization of cognitive-related activity.” Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 5(4), pp. 535–563, 1998, Dec. doi: 10.3758/bf03208834.
-
“Cortical Dynamics of Semantic Processing during Sentence Comprehension: Evidence from Event-Related Optical Signals.” Huang, J., Wang, S., Jia, S., Mo, D. & Chen, H.-C. PLoS ONE, 8(8), p. e70671, 2013, Aug. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070671.
-
“Imaging cortical dynamics of language processing with the event-related optical signal.” Tse, C.-Y., Lee, C.-L., Sullivan, J., Garnsey, S.M., Dell, G.S., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 104(43), pp. 17157–17162, 2007, Oct. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707901104.
-
“
Proof-of-concept evidence for trimodal simultaneous investigation of human brain function.” Moore, M., Maclin, E.L., Iordan, A.D., Katsumi, Y., Larsen, R.J., Bagshaw, A.P., Mayhew, S., Shafer, A.T., Sutton, B.P., Fabiani, M., Gratton, G. & Dolcos, F. Human Brain Mapping, 42(13), pp. 4102–4121, 2021, Jun. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25541. -
“Establishing the functional connectivity of the frontotemporal network in pre-attentive change detection with Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation and event-related optical signal.” Tse, C.-Y., Yip, L.-Y., Lui, T.K.-Y., Xiao, X.-Z., Wang, Y., Chu, W.C.W., Parks, N.A., Chan, S.S.-M. & Neggers, S.F.W. NeuroImage, 179, pp. 403–413, 2018, Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2018.06.053.
-
“Validation of a method for coregistering scalp recording locations with 3D structural MR images.” Whalen, C., Maclin, E.L., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. Human Brain Mapping, 29(11), pp. 1288–1301, 2008, Nov. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20465.
-
“Improving the signal-to-noise ratio of event-related optical signals.” Maclin, E.L., Low, K.A., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 26(4), pp. 47–51, 2007, Jul. doi: 10.1109/memb.2007.384095.
-
“Effects of measurement method, wavelength, and source-detector distance on the fast optical signal.” Gratton, G., Brumback, C.R., Gordon, B.A., Pearson, M.A., Low, K.A. & Fabiani, M. NeuroImage, 32(4), pp. 1576–1590, 2006, Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2006.05.030.
-
“Lagged covariance structure models for studying functional connectivity in the brain.” Rykhlevskaia, E., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. NeuroImage, 30(4), pp. 1203–1218, 2006, May. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.019.
-
“Optimum filtering for EROS measurements.” Maclin, E.L., Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. Psychophysiology, 40(4), pp. 542–547, 2003, Jul. doi: 10.1111/1469-8986.00056.
-
“The event-related optical signal (EROS) in visual cortex: Replicability, consistency, localization, and resolution.” Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. Psychophysiology, 40(4), pp. 561–571, 2003, Jul. doi: 10.1111/1469-8986.00058.
-
“Toward Noninvasive 3-D Imaging of the Time Course of Cortical Activity: Investigation of the Depth of the Event-Related Optical Signal.” Gratton, G., Sarno, A., Maclin, E., Corballis, P.M. & Fabiani, M. NeuroImage, 11(5), pp. 491–504, 2000, May. doi: 10.1006/nimg.2000.0565.
-
“Bootstrap assessment of the reliability of maxima in surface maps of brain activity of individual subjects derived with electrophysiological and optical methods.” Fabiani, M., Gratton, G., Corballis, P.M., Cheng, J. & Friedman, D. {Behavior Research Methods, Instruments, 30(1), pp. 78–86, 1998, Mar. doi: 10.3758/bf03209418.
-
“Principles, Methods, and Experimental Results.” Gratton, G., & Fabiani, M. In: Frostig, R.D., editor. In Vivo Optical Imaging of Brain Function. 2nd edition. Boca Raton (FL): CRC Press/Taylor & Francis; 2009. Chapter 15.
-
“Optical imaging of the intact human brain [Guest Editorial].” Fabiani, M., Schmorrow, D.D. & Gratton, G. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine, 26(4), pp. 14–16, 2007, Jul. doi: 10.1109/memb.2007.384090.
-
“Event-Related Brain Potentials.” Fabiani, M., Gratton, G., & Federmeier, K.D. In Cacioppo, J., Tassinary, L., & Berntson, G. (Eds.), Handbook of Psychophysiology, pp. 85 - 119, 2007, Jun. doi: 10.1017/cbo9780511546396.
-
“Optical Imaging of Brain Function.” Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. Neuroergonomics, pp. 65–81, 2006, Nov. doi: 10.1093/acprof:oso/9780195177619.003.0005.
-
“Lagged covariance structure models for studying functional connectivity in the brain.” Rykhlevskaia, E., Fabiani, M. & Gratton, G. NeuroImage, 30(4), pp. 1203–1218, 2006, May. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.11.019.
-
“Fast cerebral functional signal in the 100-ms range detected in the visual cortex by frequency-domain near-infrared spectrophotometry.” Wolf, M., Wolf, U., Choi, J.H., Toronov, V., Paunescu, L.A., Michalos, A. & Gratton, E. Psychophysiology, 40(4), pp. 521–528, 2003, Jul. doi: 10.1111/1469-8986.00054.
-
“Seeing right through you: Applications of optical imaging to the study of the human brain.” Gratton, G., Fabiani, M., Elbert, T. & Rockstroh, B. Psychophysiology, 40(4), pp. 487–491, 2003, Jul. doi: 10.1111/1469-8986.00050.
-
“The event-related optical signal: a new tool for studying brain function.” Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. International Journal of Psychophysiology, 42(2), pp. 109–121, 2001, Oct. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8760(01)00161-1.
-
“Shedding light on brain function: the event-related optical signal.” Gratton, G. & Fabiani, M. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 5(8), pp. 357–363, 2001, Aug. doi: 10.1016/s1364-6613(00)01701-0.
-
“What Triggers the Interictal Epileptic Spike? A Multimodal Multiscale Analysis of the Dynamic of Synaptic and Non-synaptic Neuronal and Vascular Compartments Using Electrical and Optical Measurements.” Arnal-Real, C., Mahmoudzadeh, M., Manoochehri, M., Nourhashemi, M. & Wallois, F. Frontiers in Neurology, 12, 2021, Feb. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.596926.
-
“Cortical hemodynamic mapping of subthalamic nucleus deep brain stimulation in Parkinsonian patients, using high-density functional near-infrared spectroscopy.” Mahmoudzadeh, M., Wallois, F., Tir, M., Krystkowiak, P. & Lefranc, M. PLOS ONE, 16(1), p. e0245188, 2021, Jan. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0245188.